20Shift: Your Daily Dose of Insight
Stay updated with the latest trends and news across various domains.
Fairly Smart: Rethinking Trust in Blockchain Contracts
Discover how to rethink trust in blockchain contracts with Fairly Smart. Uncover insights that could change your perspective!
What Makes Blockchain Contracts Trustworthy? An In-Depth Exploration
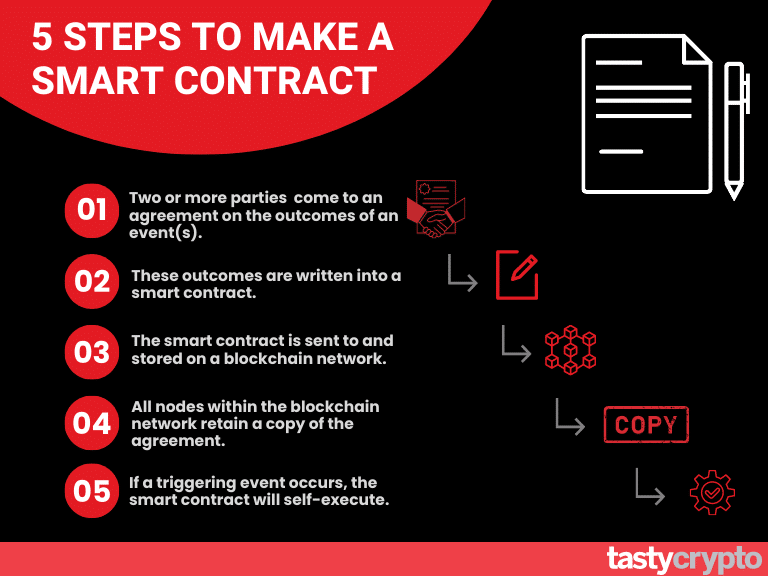
Blockchain contracts, often referred to as smart contracts, are digital agreements that automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. Their trustworthiness arises from the inherent properties of blockchain technology itself. Firstly, the decentralization aspect of blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, allowing parties to engage directly with one another. This peer-to-peer interaction reduces the chances of fraud or manipulation, as all transactions are verifiable on a public ledger. Furthermore, the immutability of blockchain ensures that once a contract is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, thereby providing a permanent and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
Moreover, the transparency offered by blockchain technology significantly contributes to the trustworthiness of smart contracts. Every transaction is visible to all participants, which fosters a sense of accountability and encourages adherence to the terms of the contract. Additionally, features like cryptographic security enhance the integrity of these contracts by ensuring that they can only be accessed or executed by authorized parties. As such, businesses and individuals exploring the use of blockchain contracts can confidently rely on their design and functionality, knowing that the principles behind these technologies uphold trust and security in digital agreements.
Counter-Strike is a popular tactical first-person shooter game that has captivated players for decades. It focuses on team-based gameplay, where players can choose to be part of either the Terrorists or Counter-Terrorists, each with specific objectives. For those looking to enhance their gaming experience, you can check out the bc.game promo code that offers great bonuses for players.
Understanding the Limitations of Trust in Blockchain Contracts
Blockchain technology is often heralded for its ability to foster trust in decentralized systems, yet an in-depth analysis reveals inherent limitations in this trust model, especially when applied to smart contracts. Smart contracts automate the execution of agreements, relying on code that operates without human intervention. However, trust in these contracts is contingent on several factors, including the integrity of the code itself. A poorly written contract, susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities, can lead to unintended consequences, undermining the very basis of trust that users place in the blockchain.
Moreover, the trust placed in blockchain contracts is further complicated by external influences, such as oracles that provide real-world data. If these oracles provide inaccurate information, the outcomes of the smart contracts can be erroneous, resulting in significant financial implications for users. Understanding the limitations of trust in blockchain contracts is crucial; it requires not only a comprehension of the technology itself but also an awareness of the potential pitfalls related to code integrity and data authenticity. As blockchain continues to evolve, enhancing the trust framework requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
How to Rethink Trust: Alternatives and Innovations in Smart Contracts
In the digital landscape, trust has become a cornerstone for successful transactions and interactions. As conventional models of trust face challenges, innovations in smart contracts offer alternative solutions that rethink how we establish reliability between parties. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the agreement are directly written into code. This technology not only reduces the need for intermediaries but also ensures transparency and security through decentralized blockchain networks. By eliminating human errors and biases, smart contracts can facilitate transactions with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
To further rethink trust, various innovations are emerging within the realm of smart contracts. For instance, platforms like Ethereum and Polkadot enable developers to create complex decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage smart contracts to function in a trustless environment. Additionally, utilizing oracles can enhance the functionality of smart contracts by providing secure and accurate external data feeds. This capability allows contracts to react to real-world events, bridging the gap between on-chain and off-chain data. As these technologies evolve, the potential for developing more robust and flexible trust models will reshape how we engage in digital transactions.